This is an article I wrote that was just published in The Mennonite magazine, about the need for Mennonites – and Christians in general – to engage and be open to the messages of the New Atheists.
Writing for different audiences is an interesting process for me. This article is specifically written for a religious audience and so my language reflects that. Even though I don’t believe in any literal sort of God or a personified God, I still find the concept of God and all the good things it can represent to be useful, powerful, and inspiring. So I hope you enjoy the article, and I think it’s a good example of the kind of approach I take when trying to gently nudge religious people to question their tradition and doctrines a bit more. After this I will resume the “M&M” series I previously started, wrapping up with the third “M” about Mennonites (aka Anabaptists) since I do mention them a lot!

Over the last ten years there has been a resurgence of atheist critique of Christianity and religion in general spurred by the “New Atheists.” This refers especially to four prominent and bestselling authors: Sam Harris (End of Faith and Letter to a Christian Nation), Richard Dawkins (The God Delusion), Christopher Hitchens (God is Not Great), and Daniel Dennett (Breaking the Spell: Religion as a Natural Phenomenon).
I first heard about them in 2007 when I picked up Harris’ Letter to a Christian Nation. It’s a strong critique of American Christianity that highlights its inconsistencies and moral shortcomings. I was impressed and moved by his obvious passion for ethics, morals, and his willingness to engage the scriptures and topics of spirituality.
Here’s a passage of his that stood out to me as very reasonable and inviting of dialogue:
“It is important to realize that the distinction between science and religion is not a matter of excluding our ethical intuitions and spiritual experiences from our conversation about the world; it is a matter of our being honest about what we can reasonably conclude on their basis. There are good reasons to believe that people like Jesus and the Buddha weren’t talking nonsense when they spoke about our capacity as human beings to transform our lives in rare and beautiful ways. But any genuine exploration of ethics or the contemplative life demands the same standards of reasonableness and self-criticism that animate all intellectual discourse.” (Harris, Letter to a Christian Nation)
I’ve personally experienced the frustration of arguments that rely purely on dogma or a particular teaching lacking any apparent understanding or context, so I empathize with Harris and also desire a straightforward conversation about religion, its strengths, and its flaws.
In other parts of his book, Harris quoted and interpreted some of Jesus’ words as support for the violence of the Old Testament, something that went against my own understanding of Jesus, the scriptures, and Anabaptist understandings of the gospel. From this, I saw the possibility for an exchange between atheists and religious people in which each could learn from the other and recognize validity in the other’s viewpoints.
As I read more of the New Atheists, I had to recognize that some of their points were correct. I was inclined to learn from them and engage their ideas instead of just fight or oppose them.
Isn’t this what Jesus did? He intentionally spent time with people different from himself, both the religious leaders and those considered outcasts or heathens by traditional religion (like atheists today).
Anabaptists emphasize loving one’s enemies, and one good way to do this is to deeply understand them and be open to the possibility that they bring something important to the table. Many atheists have good, noble motivations even though some can be angry or inflammatory.
And it goes the other way, too: Harris has certainly gotten his fair share of angry and unloving responses from Christians. We need to be honest and admit there’s a lot to be angry about when it comes to the violence, hypocrisy, judgment, and worldliness of religion.
Anabaptists are used to having minority views that challenge the status quo of the Christian majority. As a result, perhaps it can be a bit easier for us to engage in dialog with atheists.
It’s important to show outsiders that there are people within religion who care about the practical effects of their beliefs and are able to critically and rationally analyze those beliefs. Atheists are doing a good job critiquing religion, and unless religious people step up and synthesize their critiques then nothing will move forward.
The spirit blows where it will and we often see it blowing free from human rules and sin that creep into religious institutions. Certainly the spirit is active in many of the atheists who critique religion for the right reasons, and it’s interesting to think of God using atheists to correct and edify Christians.
The late Christopher Hitchens was sometimes known as one of the angrier voices of the New Atheists, but he could also write very beautifully about the bible and praise those who have sought reform from within Christianity.
In his article When the King Saved God, Hitchens expressed praise and respect for the reformers and scholars who created the King James Bible, the first bible in the English language. It was a monumental development as it let the masses finally read the bible in their own language. Previously all services and bibles were in Latin, keeping the powers of the church and interpretation in the hands of the clergy.
Perhaps surprisingly, Hitchens (as well as other atheists like Dawkins) support the teaching of the bible in public schools because they want people to read and think critically about the bible and not merely be told what it means in church.
In the article, Hitchens also gave some examples of how translating between languages can inherently involve interpretation; a specific translation could have a big impact on meaning. One of these was the Greek word ecclesia, which best translated means an independent church body, or one that can make its own rules and interpretations. This translation was favored by some in the King James commission as opposed to an interpretation of “The Church,” a single or at least highly centralized authoritative body that hands down and enforces its rules.
The latter won out, but Anabaptists have a history of the decentralized approach, following their own consciences, and searching the bible for its teachings and application in daily life and culture.
Most strikingly, at his father’s funeral, Hitchens chose to use what he called a “non-sermonizing” verse from Paul in the New Testament: “Finally, brethren, whatsoever things are true, whatsoever things are honest, whatsoever things are just, whatsoever things are pure, whatsoever things are lovely, whatsoever things are of good report; if there be any virtue, and if there be any praise, think on these things.”
He was struck by the beauty and universality of this verse, as well as the critical thinking implied by it. He felt that there have been Christians including Paul who think seriously about what is truly good and bad, beautiful and virtuous, and base their approach on that.
In his view, many Christian doctrines are not true to this, and I would point out that many were formed for political reasons supporting control, violence, and empire building. As Jesus-centered Anabaptists we should be able to ask if some parts of Christian doctrinal formation were carried out against Jesus’ command and example not to rule with power and coercion, but to lead by humble service and example.
Since some prominent atheists are willing to learn from and even be inspired by elements of Chrristianity, should we not be open to learning more about their insights, wisdom, concern for justice, and the beauty they find in life, the universe, and in their fellow human beings?
To be sure we’re not missing out on how the spirit is moving today, we need to be in touch with and understand our “enemies,” getting past rhetoric or argument by engaging in serious self-reflection and by listening to their finer points and critiques.
So perhaps you have a friend who’s an atheist. You could ask them what they really think about Christianity and why. What good do they see and what troubles them about it? Make a special effort to understand an outside viewpoint and a fresh perspective. Or, pick up one of the books by the New Atheists from the library and give it a shot.
Ultimately, we want to be informed about current thought on religion because many people rightfully have beef against it. It’s better to be engaged in the process of understanding, growing, and transformation this can bring rather than be passive bystanders oblivious to the possibility of prophetic voices coming from outside of Christianity.
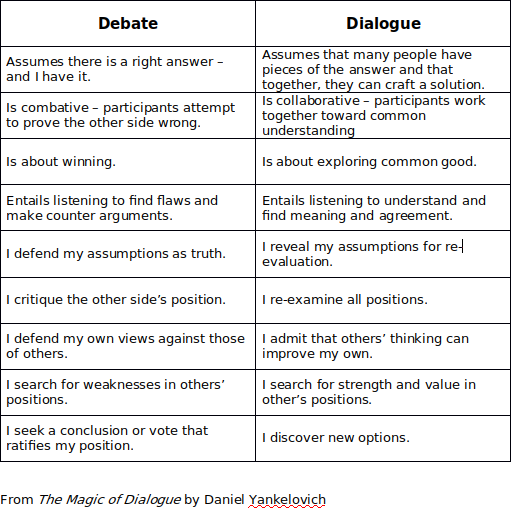 I found this interesting because I have both a dialogue (interfaith event) and a debate (on nuclear energy and climate change) coming up. Although I hope that there are elements of dialogue in the debate, it’s just the nature of the beast that there is a concrete set of points and arguments you’re trying to convince the other side (and more to the point, the audience) of. In the back of my mind, I do envision both sides of the debate forming a dialogue of sorts with the audience, and am curious how the audience will respond and what questions they have, which then potentially turns it into more of a dialogue as well.
I found this interesting because I have both a dialogue (interfaith event) and a debate (on nuclear energy and climate change) coming up. Although I hope that there are elements of dialogue in the debate, it’s just the nature of the beast that there is a concrete set of points and arguments you’re trying to convince the other side (and more to the point, the audience) of. In the back of my mind, I do envision both sides of the debate forming a dialogue of sorts with the audience, and am curious how the audience will respond and what questions they have, which then potentially turns it into more of a dialogue as well.